

Understanding the science behind bed bug treatment is critical for effective pest management in both residential and commercial settings. By exploring the biology of these resilient insects, we can better comprehend the rationale behind various treatment methods, such as heat application and chemical interventions.
While some strategies show promise, the emergence of resistance necessitates a thorough approach that combines multiple tactics.
This discussion will examine the nuances of effective treatment and prevention, revealing key insights that could make all the difference in maintaining a bed bug-free environment. What are the implications of these findings for your pest control strategy?
Understanding the biology of bed bugs is essential for effective treatment and prevention strategies. Cimex lectularius, commonly known as the bed bug, is a small, nocturnal parasitic insect that feeds on human blood.
Adult bed bugs are approximately 4 to 5 millimeters long, with a flattened, oval shape, making them adept at hiding in small crevices. They undergo a five-stage life cycle, including egg, nymph, and adult stages, with the nymphs requiring blood meals to molt.
Bed bugs are resilient, capable of surviving for months without a meal, and can reproduce rapidly, leading to swift infestations. Their primary mode of transport is through human belongings, emphasizing the importance of understanding their biology for effective control measures.
Identifying the common signs of bed bug infestation is essential for timely intervention and eradication. One of the most noticeable indicators is the presence of small, rust-colored stains on bedding and upholstery, resulting from crushed bed bugs.
Additionally, you may find tiny, white eggs or shed skins in hiding places. Bed bugs often leave a distinctive, sweet, musty odor, which can signal a larger infestation. Unexplained bites or welts on the skin, particularly in a linear pattern, should also raise concern.
These symptoms typically appear during the night, as bed bugs are nocturnal feeders. By being vigilant and recognizing these signs early, homeowners can take proactive steps to mitigate the problem before it escalates further.
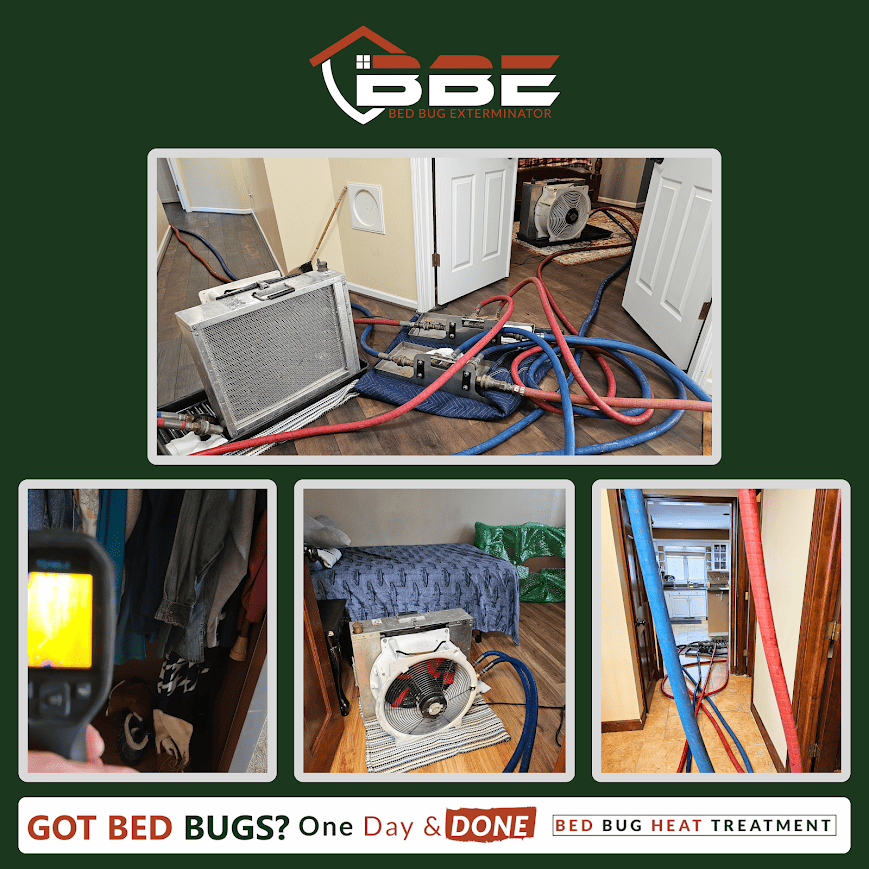
When faced with a bed bug infestation, it is essential to employ a detailed treatment strategy to effectively eliminate these pests. The primary methods of treatment include heat treatment, which raises the ambient temperature to levels lethal for bed bugs, and steam treatment, which uses high-temperature steam to target infested areas.
Vacuuming is also vital, as it physically removes bed bugs and eggs from surfaces. Additionally, encasements for mattresses and box springs can prevent bed bugs from hiding and facilitate easier monitoring.
Regular laundering of bedding and clothing at high temperatures further aids in controlling the infestation. Combining these methods often yields the best results, ensuring thorough eradication of bed bugs from your environment.
Chemical treatments are a vital component in the battle against bed bug infestations, offering targeted solutions that directly address these resilient pests. Various insecticides, including pyrethroids, neonicotinoids, and insect growth regulators, are commonly employed to disrupt the life cycle of bed bugs.
Pyrethroids act by attacking the nervous system, leading to paralysis and death, while neonicotinoids target specific receptors in the pests, effectively incapacitating them. Insect growth regulators, on the other hand, prevent bed bugs from maturing and reproducing.
It is essential to use these chemicals judiciously, as bed bugs can develop resistance to certain treatments over time. Combining chemical methods with thorough cleaning and preventive measures enhances the overall effectiveness of a detailed bed bug management strategy.

Heat treatment has emerged as an effective alternative to chemical methods in the fight against bed bug infestations. This approach involves raising the temperature of infested areas to a level that is lethal to bed bugs, typically between 120°F to 140°F (49°C to 60°C).
Research indicates that exposure to these temperatures for an adequate duration-generally around 60 minutes-can effectively eliminate all life stages of bed bugs, including eggs. Unlike chemical treatments, heat treatment penetrates various materials, guaranteeing thorough eradication within furniture, carpets, and crevices.
Additionally, it minimizes the risk of chemical resistance, a growing concern in pest management. However, it is essential to engage trained professionals to ascertain the treatment's effectiveness and safety in residential settings.
To effectively prevent future bed bug infestations, a proactive approach is essential. Regularly inspect your living spaces, including luggage, furniture, and bedding, especially after traveling or acquiring used items. Utilize protective encasements on mattresses and box springs to create a barrier against these pests.
Maintain cleanliness by vacuuming frequently and decluttering areas where bed bugs may hide. Seal cracks and crevices in walls, floors, and around baseboards to eliminate potential harborage sites. Additionally, educate yourself and others about the signs of bed bugs, ensuring prompt identification and response.
For those living in multi-unit dwellings, maintain open communication with neighbors and property management to address any concerns collectively, as collaborative efforts greatly enhance prevention strategies against future infestations.

Bed bugs do not transmit diseases to humans in the same manner as other pests such as mosquitoes or ticks. While their bites can cause discomfort, itching, and secondary infections due to scratching, they are not known carriers of infectious pathogens. The primary concern associated with bed bug infestations is the psychological distress and sleep disturbances they can cause, rather than the transmission of diseases. Effective pest management is essential to mitigate these issues.
Regular inspections for bed bugs are essential in maintaining a pest-free environment. It is advisable to check your home every 1 to 3 months, particularly in areas prone to infestations, such as bedrooms and living rooms. After traveling or staying in hotels, conduct a thorough inspection immediately upon return. Early detection is key to effective management, as it allows for prompt action before a small problem escalates into a significant infestation.
Bed bugs are highly resilient pests that can survive a range of environmental conditions, including extreme temperatures. However, they are particularly vulnerable to temperatures above 120�F (49�C) or below 0�F (-18�C). Prolonged exposure to these extremes can effectively eliminate bed bug populations. It is essential to implement temperature-based treatment methods in conjunction with other pest control strategies to guarantee thorough eradication of these resilient insects from infested areas.